Industry News
An Overview of Photovoltaic (PV) Modules and Their Applications
Photovoltaic (PV) modules are essential components in solar power systems, responsible for converting sunlight into usable electrical energy. These modules, commonly known as solar panels, play a central role in the transition toward more sustainable and decentralized energy solutions. Designed to function in a variety of environmental conditions, PV modules are used in residential, commercial, industrial, and off-grid applications.
A typical photovoltaic module consists of multiple solar cells interconnected and encapsulated within protective materials such as glass, polymers, and aluminum frames. The core of each solar cell is made from semiconductor materials, usually silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
The generated electricity can then be used immediately, stored in batteries, or converted to alternating current (AC) using inverters, depending on the system configuration. The modular design allows users to scale the energy output by combining several PV modules based on the specific energy demand.
Photovoltaic modules come in several types, each with distinct characteristics:
These modules are made from a single crystal structure. They tend to have a uniform appearance and are commonly selected for space-efficient installations.
Composed of multiple crystal structures, these modules are typically more economical to manufacture. They are widely used in residential and commercial settings.
Made by depositing photovoltaic material on a substrate, these modules are lightweight and flexible. They can be applied in building-integrated photovoltaics or portable energy solutions.
These panels can capture sunlight from both sides, increasing energy yield in suitable installations with reflective surfaces.
Each type of module is chosen based on factors such as installation space, budget, and environmental conditions.
Key Features:
Scalability: PV modules can be combined in series or parallel configurations to meet various power needs, from small off-grid systems to large solar farms.
Durability: Modules are typically built to withstand outdoor elements such as wind, rain, snow, and UV radiation, ensuring consistent operation over extended periods.
Low Operational Requirements: Once installed, PV modules require small maintenance. Occasional cleaning and periodic inspection are usually sufficient.
Adaptability: PV modules can be mounted on rooftops, integrated into building facades, installed on the ground, or used in mobile applications like boats and RVs.
Photovoltaic modules are utilized across diverse settings:
Residential Homes: Homeowners use rooftop PV modules to reduce dependence on grid electricity and lower energy expenses.
Commercial Buildings: Businesses implement solar power systems to support operations, particularly during peak hours.
Remote Areas: In off-grid regions, PV modules offer a practical power source for lighting, refrigeration, communication, and water pumping.
Public Infrastructure: PV modules are increasingly integrated into street lighting, traffic systems, and remote sensors.
Agriculture: Farmers use PV systems to power irrigation pumps and provide energy for storage facilities.
By generating electricity without combustion, photovoltaic modules contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower air pollution. Their production and disposal require attention to materials management, but the operational phase remains a cleaner alternative compared to fossil-fuel-based energy sources.
Photovoltaic (PV) modules provide a practical method of harnessing solar energy across a wide range of environments. Their adaptability, reliability, and ease of integration into different energy systems make them a valuable component in the shift toward renewable energy solutions.

Next
Applications and Advantages of New Energy Integrated Photovoltaic Prefabricated Cabins
<p>The growing focus on renewable energy and modular infrastructure has led to the development...
View More- PRODUCTS
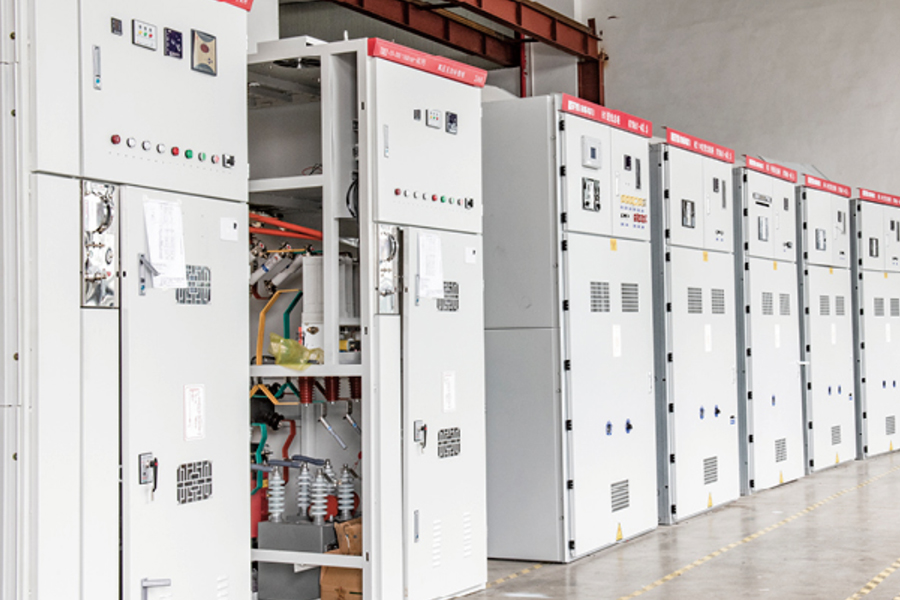
- New Energy Power Distribution Equipment
- Box Type Substation
- Cable Branch Box/Switch Station
- High Voltage Switchgear
- Low Voltage Switchgear
- Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile
- Commercial Energy Storage
- Photovoltaic Complete Box
- High Voltage Arrester
- INFORMATION
-
-
Phone+86-13868788848
+86-13356188725 -
Tel+86-0577-88810567
-
E-mail
-
AddNo. 59, Youyi Road, Xinguang Industrial Zone, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China
-
- ENQUIRE WITH US
Photovoltaic Module Manufacturer



 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 


