Industry News
Common Applications of PV Solar Panel Modules
Photovoltaic (PV) solar panel modules are key components in converting sunlight into usable electrical energy. These modules are designed to capture solar radiation and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity, which can then be used in various applications ranging from residential to large-scale commercial power generation.
A PV solar panel module consists of multiple interconnected solar cells enclosed within a protective frame and covered by glass. The cells are typically made from semiconductor materials such as silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, generating an electric current through the photovoltaic effect.
Modules are the building blocks of solar power systems. Several modules connected together form a solar array, which can be scaled to meet different power demands depending on the installation size and energy requirements.
The construction of a PV solar panel module includes several layers to protect the solar cells and optimize performance:
Solar Cells: Usually made from crystalline silicon or thin-film materials. These cells convert light to electricity.
Encapsulation Layers: These layers protect cells from moisture and mechanical damage.
Glass Cover: A tempered glass sheet protects the surface from weather elements while allowing sunlight to pass through.
Backsheet: The rear protective layer that prevents electrical leakage and physical damage.
Frame: Typically aluminum, providing structural support and mounting points.
Each component plays a crucial role in durability, efficiency, and overall functionality.
There are mainly two categories of solar cells in PV modules:
Crystalline Silicon Cells: These are the more common and come in monocrystalline and polycrystalline forms. Monocrystalline cells offer uniform appearance and generally higher efficiency, while polycrystalline cells have a speckled look and tend to be less expensive.
Thin-Film Cells: Made by depositing photovoltaic material on substrates such as glass or metal. These panels are lighter and flexible but usually have lower efficiency compared to crystalline silicon.
The choice of cell type depends on factors like cost, space availability, and specific project needs.
PV solar panel modules are widely used in:
Residential Systems: Installed on rooftops to provide electricity for homes.
Commercial Installations: Power offices, warehouses, and other business facilities.
Utility-Scale Solar Farms: Large arrays producing significant amounts of electricity fed into the grid.
Remote Locations: Off-grid systems supplying power where connection to the main grid is impractical.
The versatility of PV modules makes them suitable for a broad range of energy solutions.
Several factors influence the performance of PV solar panel modules:
Sunlight Intensity and Angle: The amount of sunlight and its angle relative to the panel affect energy generation.
Temperature: Higher temperatures may reduce module efficiency.
Shading: Partial shading can significantly decrease output.
Quality and Design: Advanced materials and design features can improve durability and conversion efficiency.
Proper installation and maintenance can help big the lifespan and productivity of PV modules.
Installing PV solar panels requires considerations such as site orientation, roof strength, and electrical integration. Panels should face the sun for good exposure, often oriented toward the equator.
Routine maintenance involves cleaning dust and debris from the surface, inspecting wiring connections, and monitoring performance to detect any degradation early.
PV solar panel modules serve as the foundation of solar energy systems, transforming sunlight into electricity in a sustainable manner. Understanding their construction, types, and operational factors is essential for designing efficient and reliable solar installations for various applications.

Next
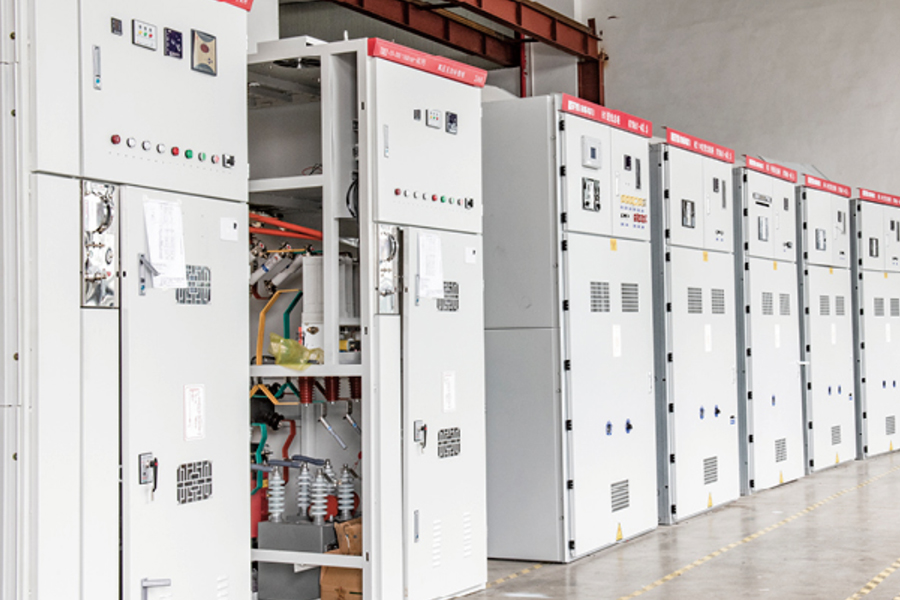
Operating Principles of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
<p>An <a href="/product/engineering-vacuum-circuit-breaker/" target="_blank&...
View More- PRODUCTS
- New Energy Power Distribution Equipment
- Box Type Substation
- Cable Branch Box/Switch Station
- High Voltage Switchgear
- Low Voltage Switchgear
- Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile
- Commercial Energy Storage
- Photovoltaic Complete Box
- High Voltage Arrester
- INFORMATION
-
-
Phone+86-13868788848
+86-13356188725 -
Tel+86-0577-88810567
-
E-mail
-
AddNo. 59, Youyi Road, Xinguang Industrial Zone, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China
-
- ENQUIRE WITH US
Photovoltaic Module Manufacturer



 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 


