Industry News
Safety and Maintenance of High Voltage Switchgear
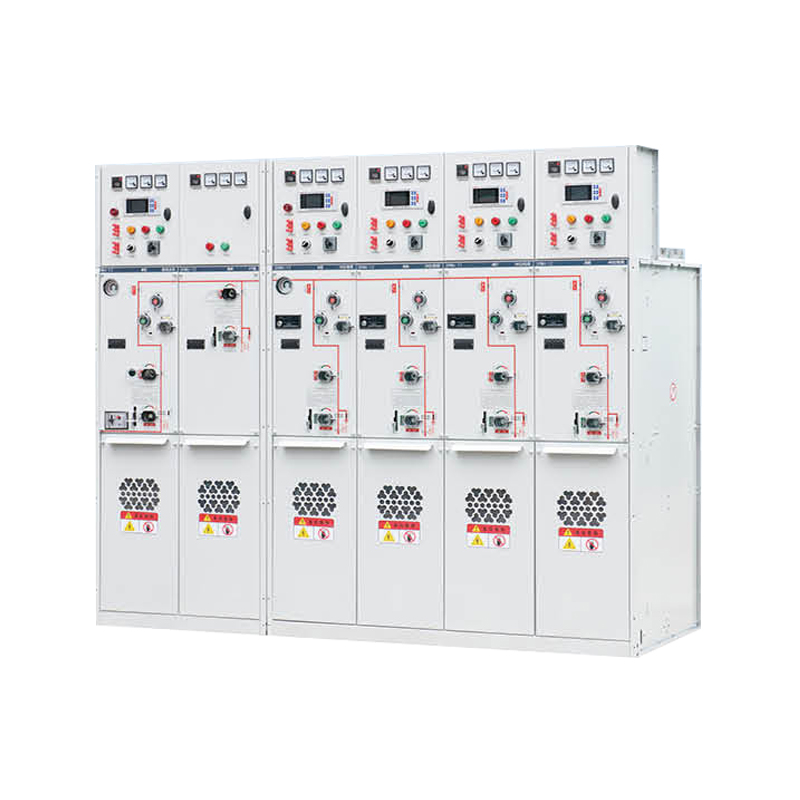
High voltage switchgear is a crucial component in electrical power systems, especially in the transmission and distribution of electricity over long distances. This equipment is designed to control, protect, and isolate electrical circuits operating at high voltages, ensuring the reliable and safe delivery of power to various end-users.
The main purpose of high voltage switchgear is to manage the flow of electrical energy within a power grid. It provides a means to switch circuits on or off under normal operating conditions or during faults. This helps protect the equipment and maintain system stability by isolating faulty sections from the rest of the network.
High voltage switchgear includes devices such as circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and protective relays. These devices respond to abnormal conditions like short circuits or overloads by interrupting the current flow, preventing damage to transformers, cables, and other critical infrastructure.
High voltage switchgear can be categorized based on the voltage levels they handle, typically ranging from medium voltage (above 1 kV) to extra-high voltage levels used in transmission networks. Different types of switchgear are designed to suit various applications, including:
Air Insulated Switchgear (AIS): Uses air as the insulating medium between live components and grounded parts. It is common in outdoor substations.
Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS): Uses sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas to insulate components, allowing for more compact designs suitable for space-limited areas.
Key components of high voltage switchgear include:
Circuit Breakers: Devices that interrupt current flow during faults to protect the system.
Disconnectors: Used to isolate parts of the circuit for maintenance, ensuring safety for personnel.
Current and Voltage Transformers: Measure electrical parameters for monitoring and protection.
Protective Relays: Detect abnormal electrical conditions and trigger breakers to operate.
The design of high voltage switchgear involves careful attention to electrical, mechanical, and environmental factors. Key considerations include:
Insulation: Proper insulation prevents electrical arcs and flashovers that could cause equipment failure or safety hazards.
Mechanical Durability: Components must withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions such as temperature variations, humidity, and pollution.
Safety: Switchgear enclosures and interlocks protect operators from electrical shocks and ensure safe operation.
Maintenance Accessibility: The design should facilitate routine inspections, testing, and repairs without compromising system uptime.
High voltage switchgear is widely used in electrical substations, power plants, and large industrial facilities. It is essential for:
Power Transmission: Controlling the flow of electricity over high voltage transmission lines.
Distribution Networks: Managing the delivery of power from substations to local distribution systems.
Industrial Power Systems: Protecting critical machinery and ensuring a reliable power supply in manufacturing plants and processing facilities.
Installing high voltage switchgear requires adherence to strict safety and technical standards. Proper site preparation, grounding, and environmental controls are important to ensure long-term reliability.
Operators typically use switchgear to:
Energize or de-energize circuits safely.
Isolate equipment for maintenance.
Respond quickly to faults to small downtime and equipment damage.
Automated control and monitoring systems increasingly integrate with high voltage switchgear to improve response times and system efficiency.
High voltage switchgear plays a fundamental role in electrical power systems by controlling and protecting high voltage circuits. Its reliable operation is vital for the stability and safety of power grids.

Next
Design and Construction Features of PV Distribution Boxes
<p>A <a href="/product/photovoltaic-complete-box/" target="_blank">p...
View More- PRODUCTS
- New Energy Power Distribution Equipment
- Box Type Substation
- Cable Branch Box/Switch Station
- High Voltage Switchgear
- Low Voltage Switchgear
- Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile
- Commercial Energy Storage
- Photovoltaic Complete Box
- High Voltage Arrester
- INFORMATION
-
-
Phone+86-13868788848
+86-13356188725 -
Tel+86-0577-88810567
-
E-mail
-
AddNo. 59, Youyi Road, Xinguang Industrial Zone, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China
-
- ENQUIRE WITH US
Photovoltaic Module Manufacturer



 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 


