Industry News
Understanding the Role of Porcelain Clad Vacuum Interrupter Circuit Breakers in Power Systems
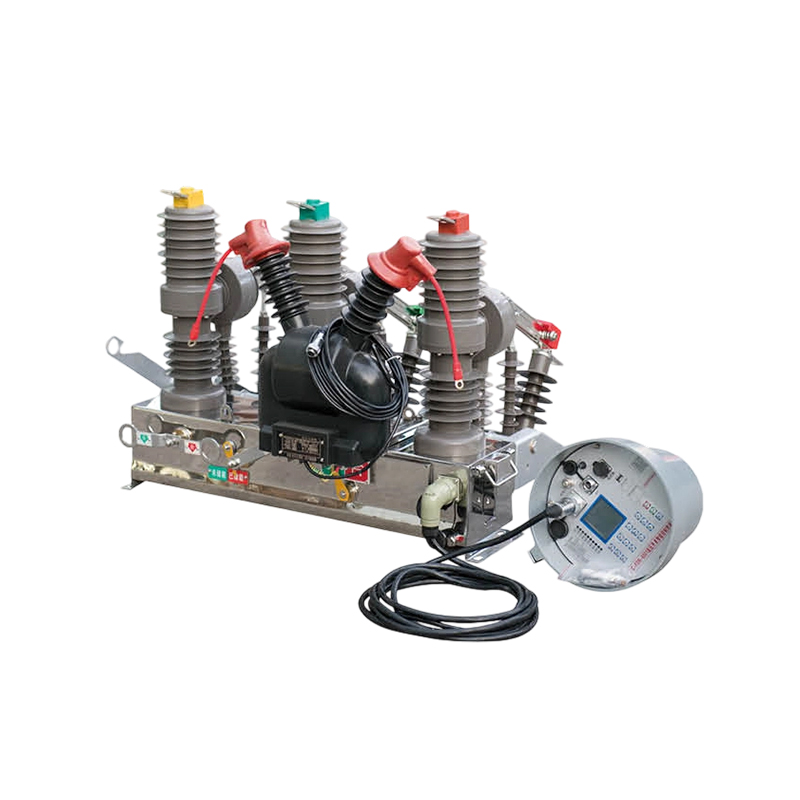
A Vacuum Interrupter Circuit Breaker (VICB) is a type of circuit protection device used primarily in medium-voltage power distribution systems. It utilizes a vacuum as the arc-quenching medium to interrupt current flow during fault conditions. This technology has become a reliable option in both industrial and utility-grade electrical networks due to its compact design, dependable performance, and low maintenance requirements.
The key component of a vacuum interrupter circuit breaker is the vacuum interrupter chamber, where the current is interrupted. During normal operation, the contacts inside the interrupter remain closed, allowing current to pass through. When a fault is detected, the breaker mechanism opens the contacts.
As the contacts separate, an arc forms between them. In a vacuum environment, the absence of gas or air prevents the arc from sustaining itself. The electrons and ions generated during the arcing process are quickly dispersed due to the high dielectric strength of the vacuum, effectively extinguishing the arc in a very short time.
Once the arc is extinguished, the circuit remains open until it is manually or automatically closed again after fault clearance.
A typical vacuum interrupter circuit breaker consists of the following key parts:
Vacuum Interrupter Chamber: Contains the fixed and moving contacts in a sealed, evacuated enclosure.
Operating Mechanism: Applies force to open or close the contacts, either manually or via an electrical actuator.
Insulating Housing: Encases the interrupter and mechanism, providing protection and electrical insulation.
Control and Sensing Units: Monitor electrical conditions and send signals to operate the breaker during fault conditions.
Vacuum interrupters operate at high speed, breaking current within milliseconds, small the risk of damage to other components.
Due to the nature of arc formation in a vacuum, the contact surfaces experience less wear, resulting in extended service life.
The sealed vacuum chamber prevents contamination, corrosion, and moisture ingress, reducing the frequency of maintenance inspections.
The design allows for a smaller footprint, making it suitable for switchgear applications where space is limited.
Compared to air or oil-based breakers, vacuum breakers operate with reduced noise levels during interruption.
Vacuum interrupter circuit breakers are widely used in:
Power Distribution Systems: Suitable for medium-voltage distribution networks in commercial and industrial buildings.
Substations: Used to manage and protect feeders, transformers, and busbars.
Motor Control Centers: Effective in interrupting high inrush current during motor startup or faults.
Renewable Energy Systems: Applied in wind and solar farms to protect equipment and maintain system stability.
Railway Electrification: Employed in traction substations to manage medium-voltage circuits.
Vacuum interrupter circuit breakers are designed to meet established electrical safety standards and performance criteria. Proper insulation coordination, mechanical interlocking, and overcurrent protection are integrated into the system to ensure reliable operation. Periodic inspection of mechanical parts and insulation resistance testing is recommended to verify functional integrity.
The vacuum interrupter circuit breaker provides an effective solution for medium-voltage power protection and control. By using a vacuum as the arc-quenching medium, it delivers fast, efficient current interruption with small maintenance needs. Its application across various sectors demonstrates its reliability in modern electrical systems, where safe and stable power distribution is essential.

Next
Features and Applications of Large Low Voltage Wire Junction Boxes
<p>A <a href="/product/" target="_blank">Large Low Voltage Wire Junc...
View More- PRODUCTS
- New Energy Power Distribution Equipment
- Box Type Substation
- Cable Branch Box/Switch Station
- High Voltage Switchgear
- Low Voltage Switchgear
- Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile
- Commercial Energy Storage
- Photovoltaic Complete Box
- High Voltage Arrester
- INFORMATION
-
-
Phone+86-13868788848
+86-13356188725 -
Tel+86-0577-88810567
-
E-mail
-
AddNo. 59, Youyi Road, Xinguang Industrial Zone, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China
-
- ENQUIRE WITH US
Photovoltaic Module Manufacturer



 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 


