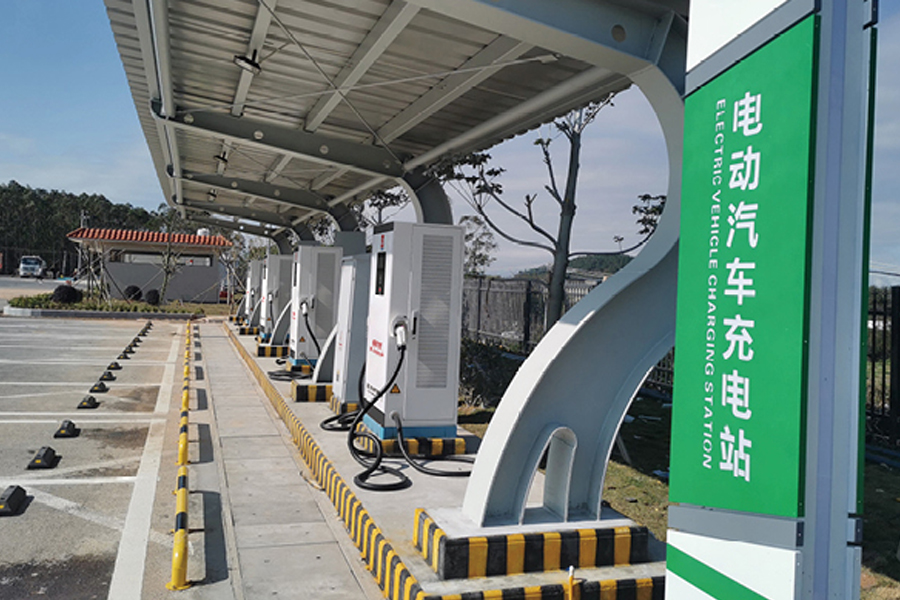
Distributed photovoltaic power stations have moved from pilot projects to widely deployed energy assets across residenti...
READ MORELow Voltage Switchgear Supplier
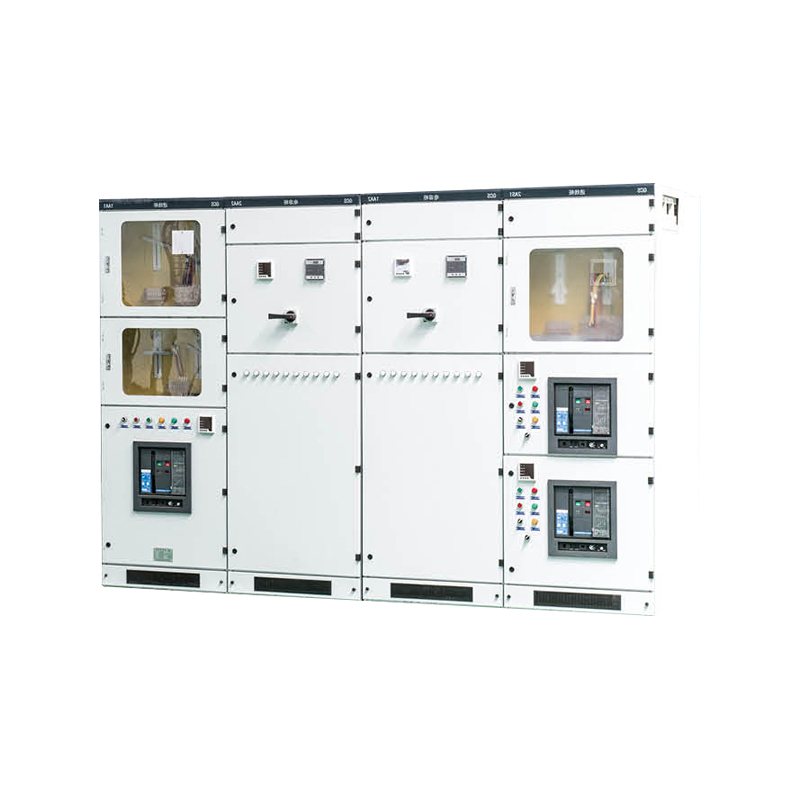
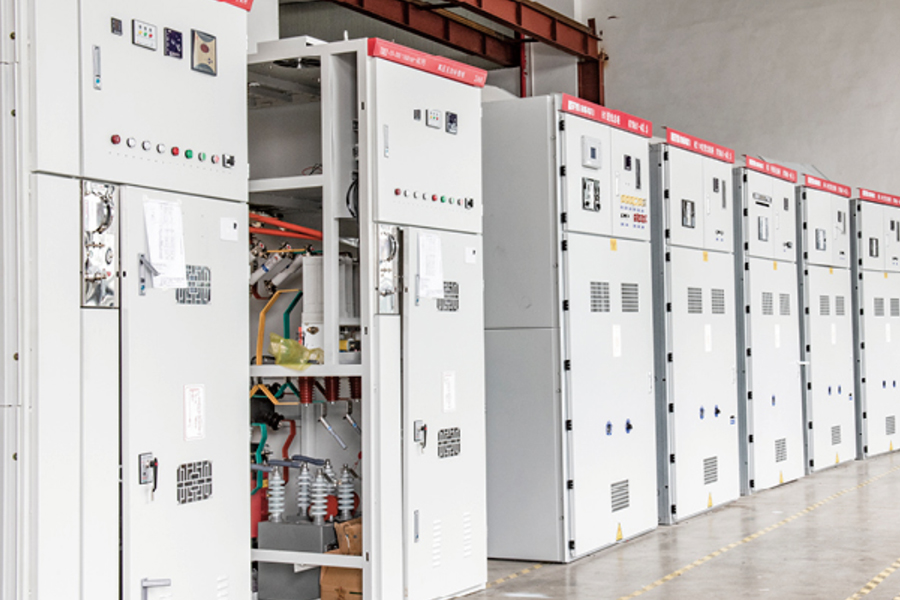
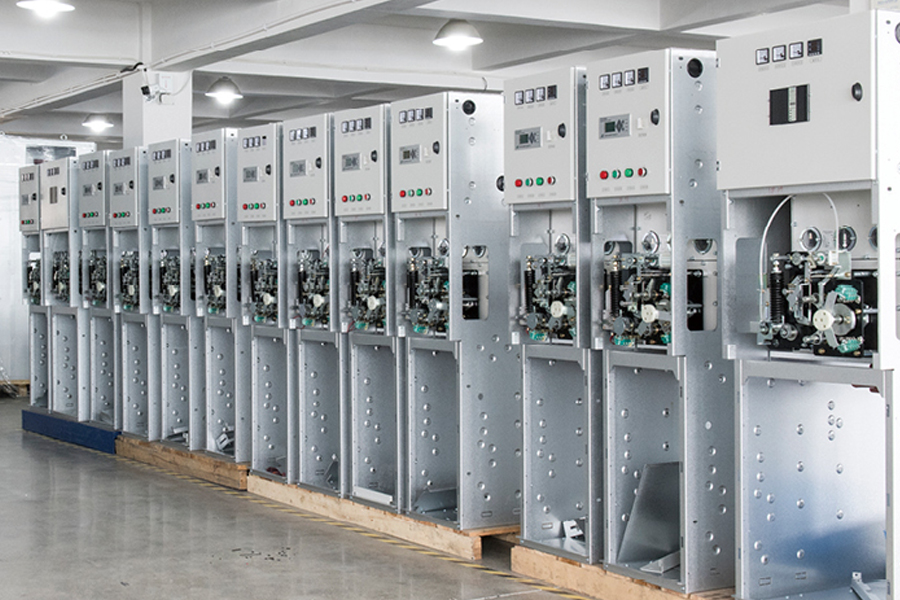
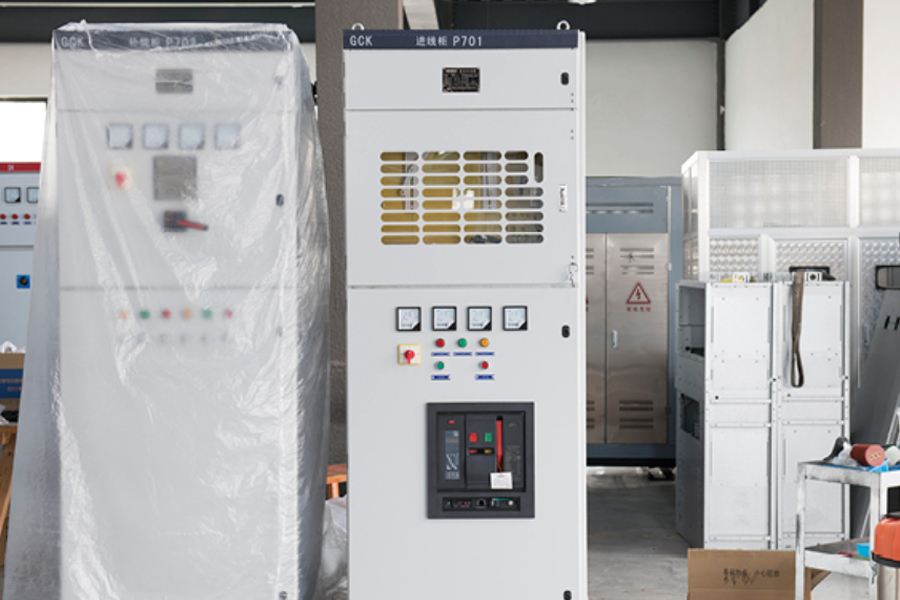
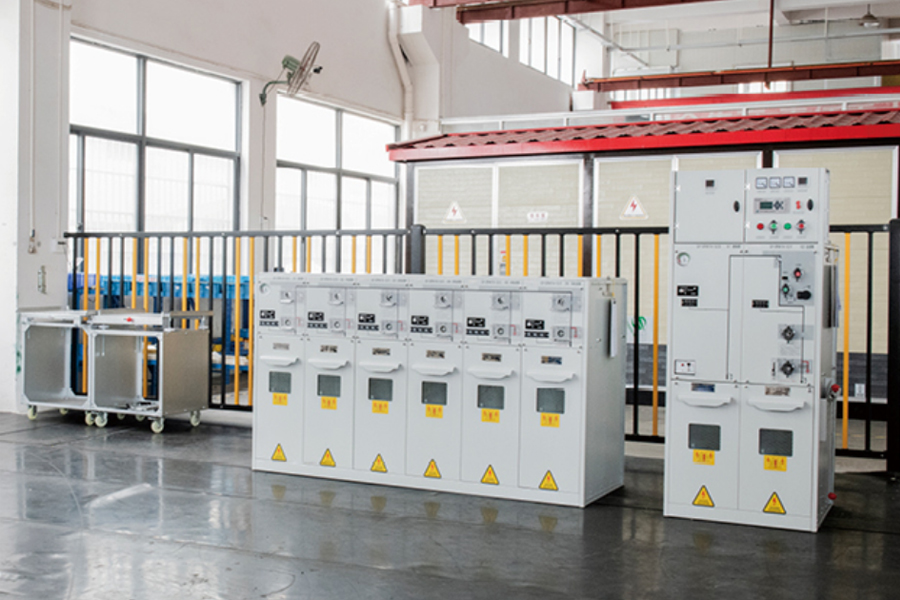
Low Voltage Switchgear is an essential part of electrical distribution systems, used to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment operating at voltages up to 1,000V AC or 1,500V DC.
Advantages
One of the primary advantages of low voltage switchgear is its comprehensive protection. It safeguards personnel and equipment by quickly isolating faulty circuits during overloads, short circuits, or earth faults. This ensures system continuity, minimizes downtime, and prevents costly damage.
Its modular design allows for easy expansion or reconfiguration, making it highly adaptable to evolving power needs. This is particularly valuable in facilities experiencing growth or layout changes. The space-saving structure also contributes to efficient equipment room planning, especially in densely packed environments.
Low voltage switchgear offers operational safety, featuring arc-resistant designs, interlocking systems, and enhanced insulation that protect users during routine operations and maintenance. Many units are also intelligent-ready, supporting remote monitoring, data logging, and integration into building management systems (BMS) or SCADA platforms.
Features
Low voltage switchgear is known for its durability, versatility, and ease of maintenance. Constructed using high-quality materials such as galvanized steel or aluminum alloy, it provides long-term performance even in challenging environments. With IP-rated enclosures, it offers protection against dust, moisture, and other external contaminants, making it suitable for both indoor and semi-outdoor applications.
Internally, it includes circuit breakers, contactors, meters, and busbars, arranged in a clearly labeled and accessible layout. This not only improves serviceability but also supports safe, efficient operations. Advanced models feature digital interfaces, touchscreen HMIs, and communication modules for real-time control and diagnostics.
Low voltage switchgear can be custom-configured to meet specific load, space, and operational requirements. Its energy-efficient operation, compact footprint, and reliable fault-handling performance make it a preferred solution for modern power distribution needs.
Search
Categories
-
New Energy Power Distribution Equipment(6)
-
Box Type Substation(3)
-
Cable Branch Box/Switch Station(3)
-
High Voltage Switchgear (23)
-
Low Voltage Switchgear(16)
-
Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker(2)
-
New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile(9)
-
Commercial Energy Storage(3)
-
Photovoltaic Complete Box(8)
-
High Voltage Arrester(54)
-
-
Integrated photovoltaic inverters have become a central component in many solar power installations, combining power con...
READ MORE -
Photovoltaic modules are evaluated primarily by their electrical performance, durability under environmental stress, and...
READ MORE -
Thermal management is a broad concept in electronics and industrial systems, encompassing various cooling methods such a...
READ MORE
A Low Voltage Switchgear assembly is a modular system of electrical components designed to control, protect, and isolate circuits operating at voltages typically below 1 kV. Housed within a metal enclosure, it integrates devices such as molded‑case circuit breakers, contactors, fuses, relays, and busbars. The switchgear enables safe distribution of power by interrupting overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. Door interlocks and insulating barriers reduce the risk of accidental contact, while standardized mounting rails simplify installation and expansion.
Overview of Low Voltage Distribution Cabinets
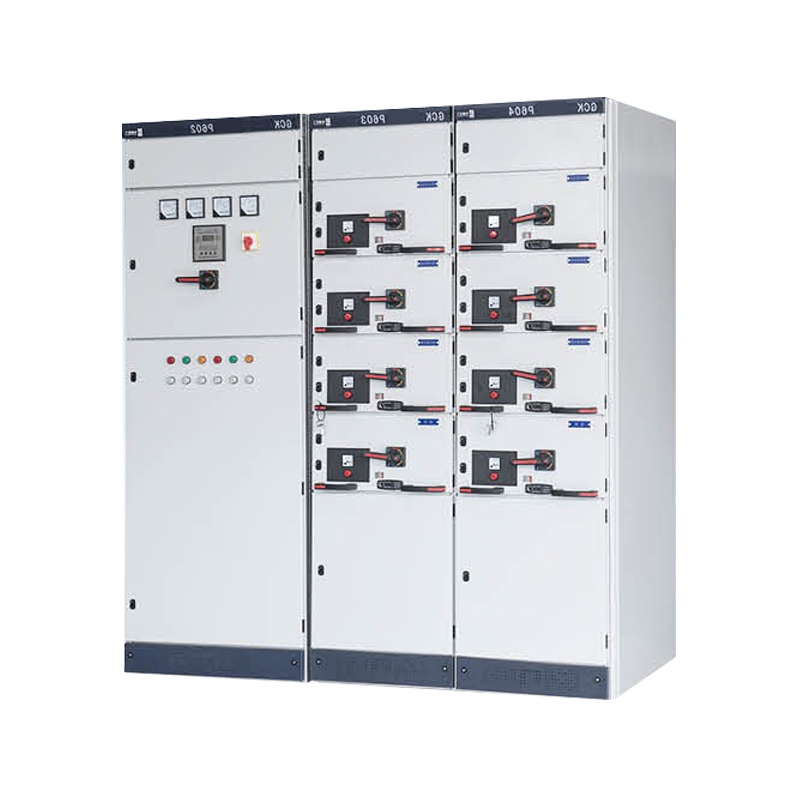
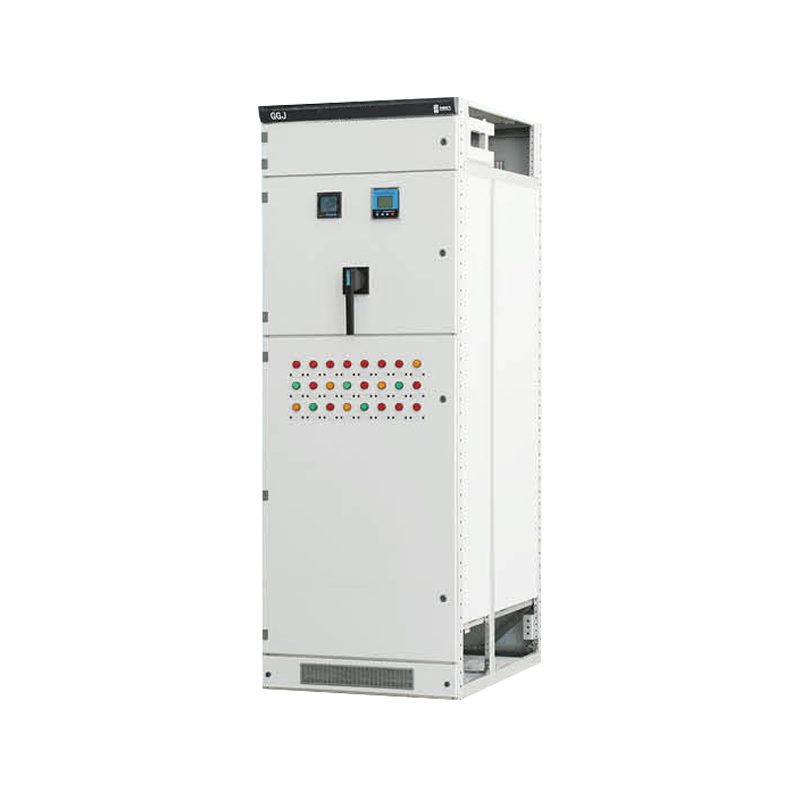
A Low Voltage Distribution Cabinet is an enclosed assembly designed to receive, distribute, and protect electrical power in systems operating below 1 kV. Constructed from sheet steel or corrosion‑resistant aluminum, the cabinet houses key components such as circuit breakers, distribution blocks, busbars, surge protection devices, and control relays. Incoming power enters through a main breaker or fused disconnect, then travels along insulated busbars to individual feeders. Each feeder circuit is safeguarded by its own protective device, isolating overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
The cabinet’s interior layout is organized to ensure clear separation between live parts and wiring channels, reducing the risk of accidental contact during operation or maintenance. Removable front panels and hinged doors provide access to equipment for inspection or replacement, while gaskets and seals around doors and cable entry points guard against dust and moisture. Ventilation slots or filtered air inlets may be included to prevent heat buildup, ensuring components remain within their rated temperature range.
Installation involves securing the cabinet to a stable surface or mounting frame, grounding the enclosure, and routing incoming and outgoing cables through conduit or properly sized cable glands. Standardized mounting rails allow for modular expansion if additional circuits are required. Control wiring for auxiliary devices or external monitoring systems can be terminated on designated terminal blocks, enabling integration with building management or supervisory control systems.
Routine maintenance is centered on visual inspection of insulation, verification of torque settings on busbar connections, and testing of protective devices using primary or secondary injection methods. Cleaning of dust from vents and interior surfaces helps maintain cooling efficiency.
Design and Sealing Features of Dustproof Electrical Boxes
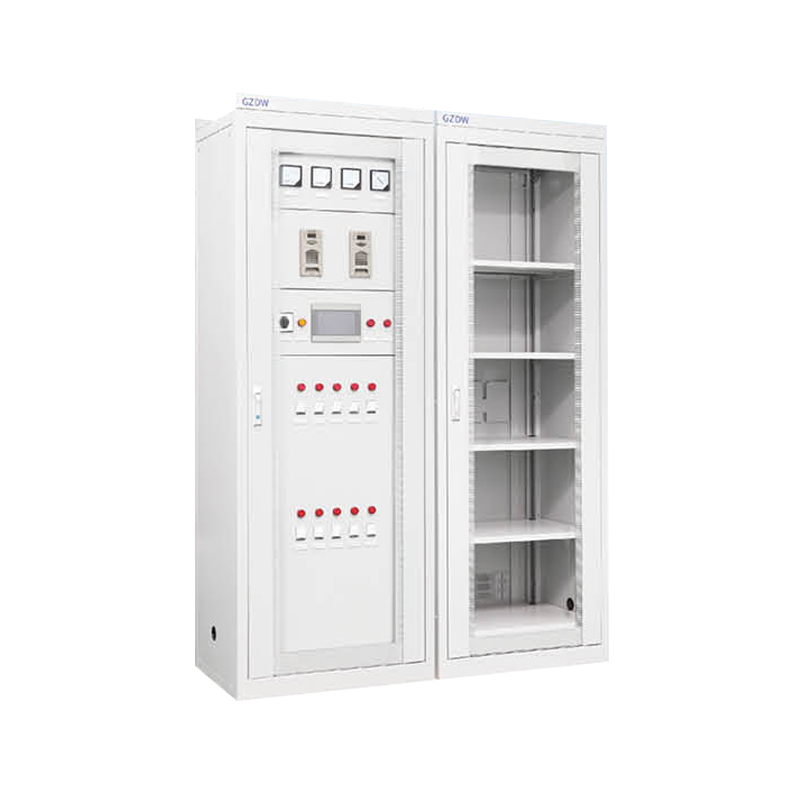
A Dustproof Power Box is a sealed enclosure engineered to protect electrical components and connections from particulate ingress in environments prone to airborne debris. Typically fabricated from high‑density polymers or powder‑coated metals, the box features an ingress protection rating of IP55 or higher, ensuring that dust particles cannot enter and compromise internal circuits. The enclosure can house terminal blocks, small breakers, transformers, control relays, and wiring junctions.
Entry and exit points for cables use gasketed cable glands or conduit connectors, preserving the seal while allowing for secure cable routing. Internally, mounting plates or DIN rails are provided to organize components neatly, maintaining adequate clearance between live elements and the enclosure walls. A hinged or fully removable lid with a silicone rubber gasket ensures quick access for assembly, inspection, or repairs, while retaining the dustproof integrity when closed.
This type of power box is commonly used in manufacturing plants, woodworking shops, grain processing facilities, and outdoor kiosks where airborne dust could otherwise pilot to equipment failure. Its application can extend to solar array junctions in desert locations, where fine sand and dust pose a risk.
Installation includes mounting the enclosure on a stable surface, routing cables through sealed glands, and properly grounding the case. Periodic maintenance involves checking gasket condition, tightening gland seals, and removing any external buildup of dust to prevent clogging of vents if present.


 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 



























