Industry News
Exploring Liquid Cooled Temperature Control Systems
Thermal management is a broad concept in electronics and industrial systems, encompassing various cooling methods such as air cooling, liquid cooling, heat pipes, and phase change materials. Among these, liquid cooling has gained attention for its higher heat transfer efficiency and ability to maintain stable operating temperatures in high-performance applications. Liquid cooled temperature control systems(You can click here) are widely used in data centers, high-performance computing, electric vehicle batteries, and industrial equipment. The global liquid cooling systems market is valued at around USD 7 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach over USD 12 billion by 2032, driven by demand for efficient thermal management solutions.

At the core of these systems are several critical components that ensure efficient thermal regulation. The coolant distribution unit (CDU) serves as the central hub, regulating the flow and temperature of the cooling liquid throughout the system. It monitors liquid pressure and temperature, ensuring consistent thermal performance and protecting connected components from overheating. Complementing the CDU, the cooling pump maintains the required flow rate, moving liquid through heat-generating elements to heat exchangers or radiators. The pump’s reliability and flow control directly influence the system’s ability to respond to varying thermal loads.
A key element in liquid cooling is the cold plate, which interfaces directly with heat sources such as CPUs, GPUs, or battery modules. Cold plates are designed to maximize surface contact with components, allowing efficient heat transfer into the circulating coolant. In water-cooled systems, cold plates typically use water-based fluids, which offer good thermal conductivity and low viscosity for effective circulation. Oil cooling, often implemented in immersion systems, submerges components in dielectric oil. Oil’s lower thermal conductivity compared to water can be offset by its ability to reach all surfaces of submerged components, eliminating hotspots and allowing for simplified system design.
The heat exchanger completes the loop by transferring heat from the liquid to the environment, usually through air or secondary coolant loops. Effective heat exchanger design ensures stable exit temperatures, minimizing thermal fluctuations and maintaining optimal operating conditions. The combination of CDU, pump, cold plate, and heat exchanger determines the overall efficiency and responsiveness of a liquid cooled temperature control system.
Liquid cooling adoption is increasing across several sectors. For example, over 65% of new data centers now integrate liquid cooling technologies to meet increasing thermal demands and improve operational efficiency. Direct liquid cooling solutions account for more than 68% of the market revenue share in 2024, reflecting industry preference for high-performance cooling.
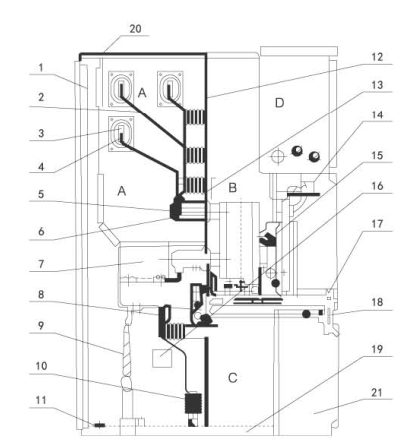
Research and development in liquid cooling are also increasingly focusing on intelligent control strategies. AI and reinforcement learning techniques are being applied to dynamically adjust coolant flow, pump speed, and temperature set points in real time. This allows the system to respond to changing workloads and thermal profiles, improving energy efficiency while maintaining component reliability. Advanced monitoring and predictive algorithms can anticipate thermal spikes, reducing risk and enabling more efficient operation in complex environments such as data centers and high-density electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: What is the main difference between water cooling and oil cooling in liquid cooled temperature control systems?
Water cooling uses water-based fluids in cold plates for high thermal conductivity and low viscosity, ideal for targeted heat sources. Oil cooling submerges components in dielectric oil, covering all surfaces and reducing hotspots, though oil transfers heat slightly slower than water.
- Q2: What are the key components of a liquid cooled temperature control system?
The primary components include the coolant distribution unit (CDU), cooling pump, cold plate, and heat exchanger. Each plays a vital role in maintaining consistent temperature and flow throughout the system.
- Q3: How does AI improve liquid cooled temperature control systems?
AI and reinforcement learning can dynamically adjust coolant flow and pump speed, responding to thermal changes in real time. This improves energy efficiency, maintains optimal temperatures, and anticipates workload variations to prevent overheating.

Next
Mobile Energy Storage Charging Pile Solutions
<p>The <strong><a href="https://www.hp-electric.com/product/new-energy-vehicle-f...
View More- PRODUCTS
- New Energy Power Distribution Equipment
- Box Type Substation
- Cable Branch Box/Switch Station
- High Voltage Switchgear
- Low Voltage Switchgear
- Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile
- Commercial Energy Storage
- Photovoltaic Complete Box
- High Voltage Arrester
- INFORMATION
-
-
Phone+86-13868788848
+86-13356188725 -
Tel+86-0577-88810567
-
E-mail
-
AddNo. 59, Youyi Road, Xinguang Industrial Zone, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China
-
- ENQUIRE WITH US
Photovoltaic Module Manufacturer



 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 


