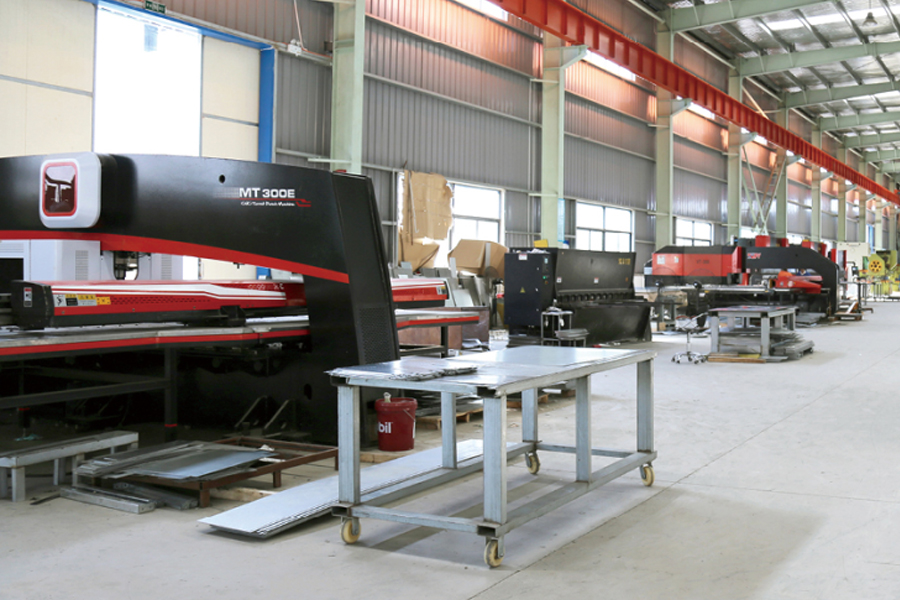
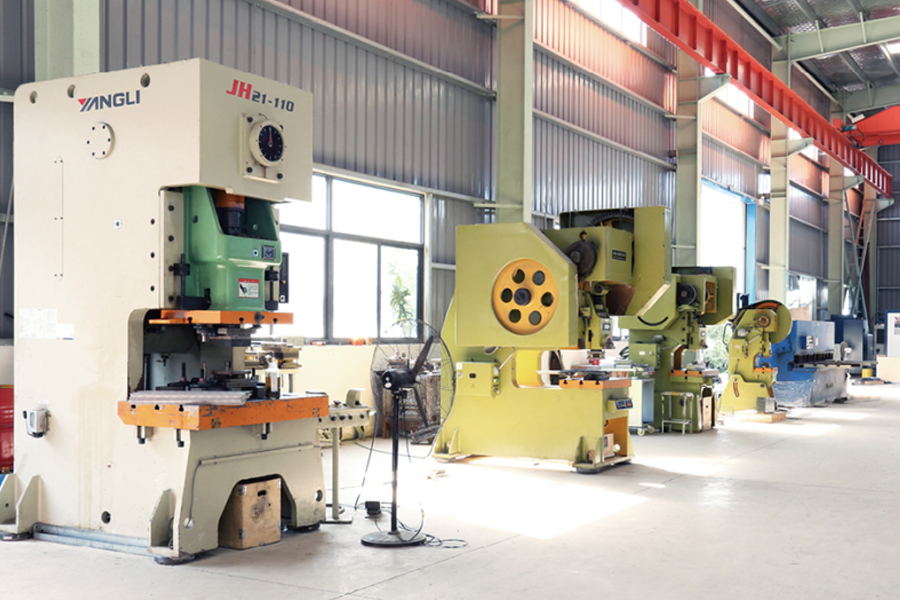
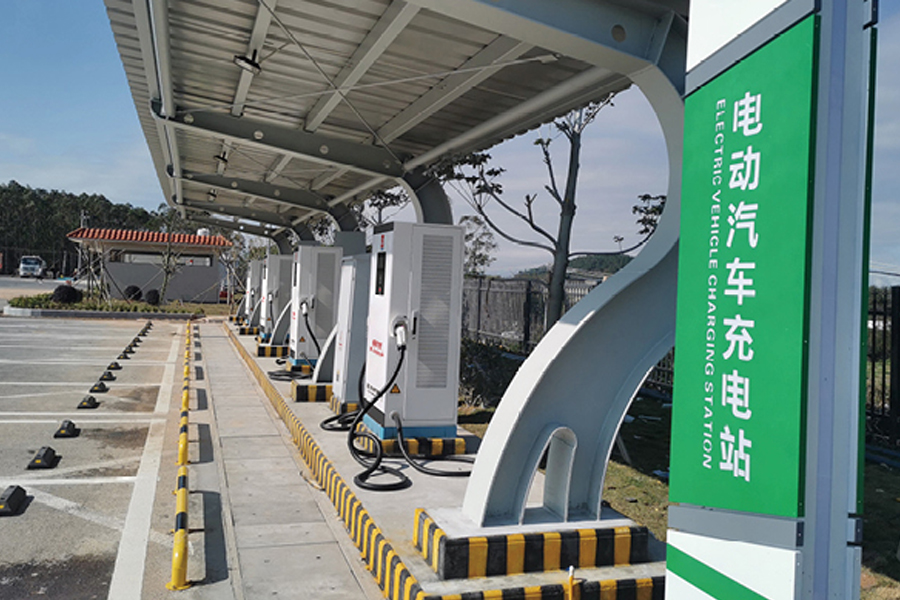
Distributed photovoltaic power stations have moved from pilot projects to widely deployed energy assets across residenti...
READ MOREUnderground IP68 Protection Cable Docking Box Factory
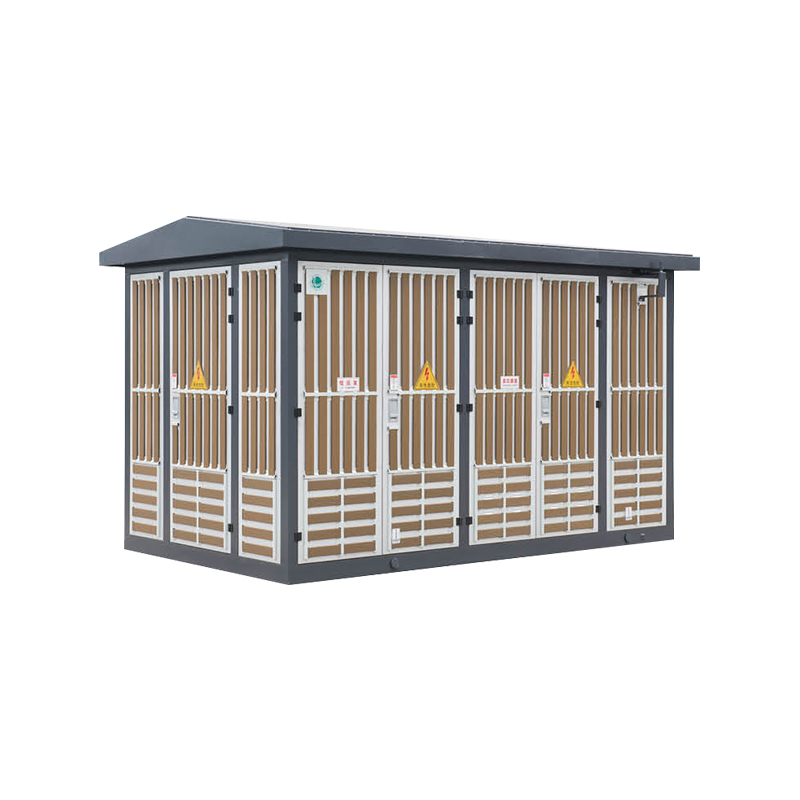
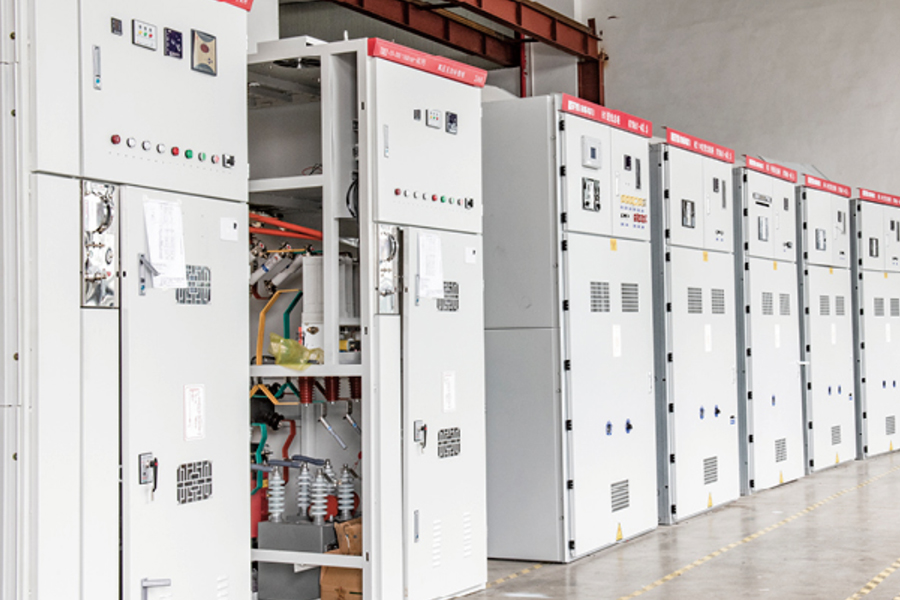
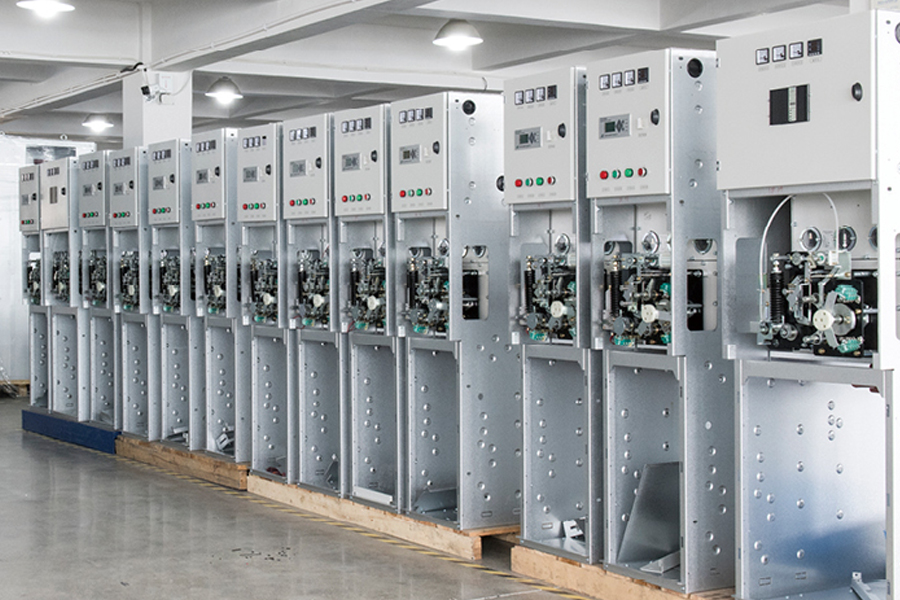
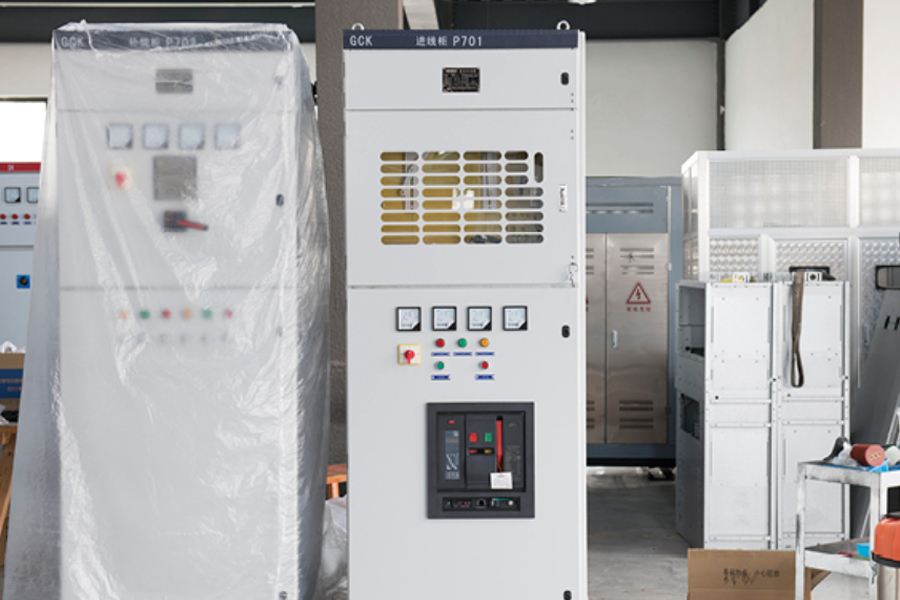
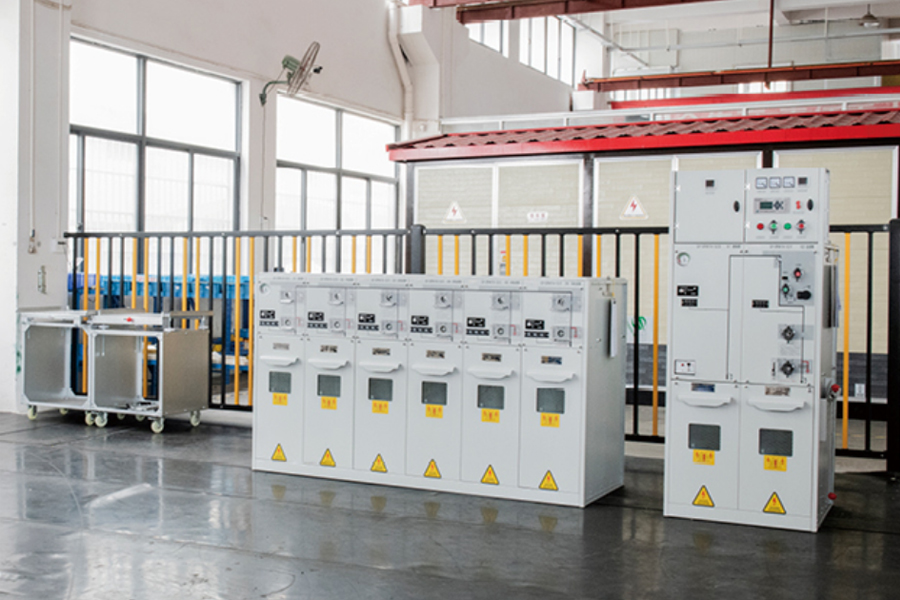
A Box Type Substation, also known as a compact substation or prefabricated substation, is an integrated power distribution solution that combines high-voltage switchgear, transformer, and low-voltage distribution equipment in a single, enclosed unit. Designed for modern energy systems, it offers a compact and modular approach to power transformation and distribution, especially in areas where space, efficiency, and installation speed are critical. Compared to traditional substations, the box-type model significantly reduces on-site construction time and operational complexity while ensuring safe and reliable power delivery.
Application
Box Type Substations are widely used in urban and rural power distribution networks, particularly in fast-developing regions where energy infrastructure needs to be deployed rapidly. They are essential in residential communities, commercial complexes, and industrial zones, providing localized voltage transformation and energy distribution. Their enclosed design makes them ideal for outdoor applications, such as in wind and solar farms, temporary construction sites, and public transportation systems like metro stations or airports.
Features
The Box Type Substation is known for being compact, modular, efficient, and durable. Its space-saving structure enables installation in areas with limited land availability. The fully enclosed design ensures weather resistance, dust-proofing, and safety against unauthorized access, making it suitable for harsh outdoor environments.
It features high thermal insulation, low noise operation, and fire-retardant materials, enhancing both safety and environmental compatibility. The plug-and-play design allows for rapid commissioning and minimal on-site work. Advanced models come with intelligent monitoring systems, enabling real-time diagnostics, remote fault detection, and predictive maintenance.
Constructed using galvanized steel or stainless steel enclosures, the substation offers long-lasting protection and requires minimal maintenance. With strong customization options, it can be tailored for various voltage levels, transformer capacities, and climate conditions.
Search
Categories
-
New Energy Power Distribution Equipment(6)
-
Box Type Substation(3)
-
Cable Branch Box/Switch Station(3)
-
High Voltage Switchgear (23)
-
Low Voltage Switchgear(16)
-
Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker(2)
-
New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile(9)
-
Commercial Energy Storage(3)
-
Photovoltaic Complete Box(8)
-
High Voltage Arrester(54)
-
-
Integrated photovoltaic inverters have become a central component in many solar power installations, combining power con...
READ MORE -
Photovoltaic modules are evaluated primarily by their electrical performance, durability under environmental stress, and...
READ MORE -
Thermal management is a broad concept in electronics and industrial systems, encompassing various cooling methods such a...
READ MORE
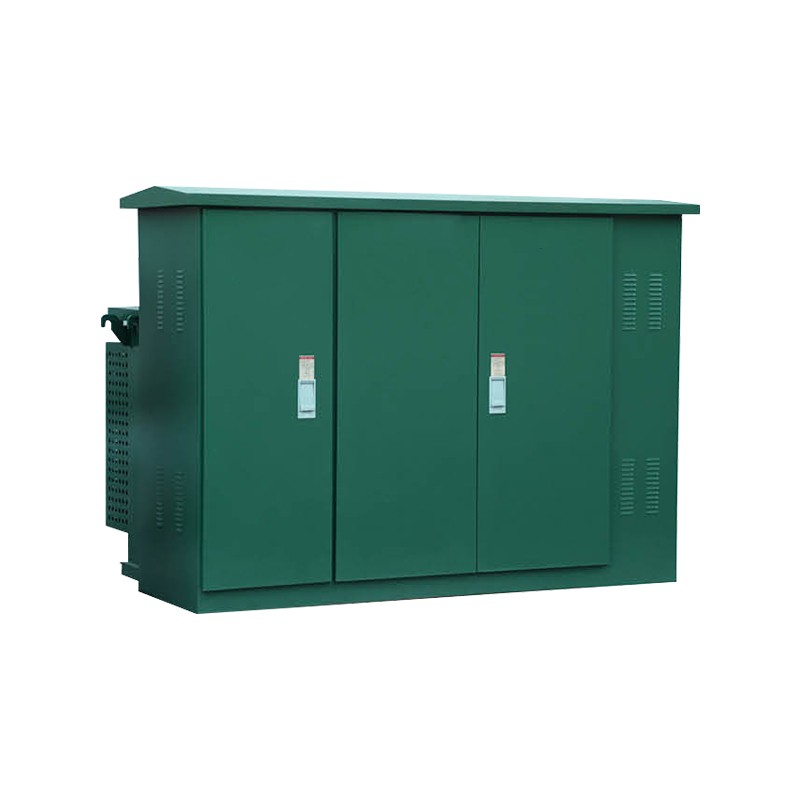
A Box Type Substation is a prefabricated electrical unit designed to transform voltage levels and distribute power in compact locations. Housed within a weatherproof enclosure, it integrates a transformer, protection devices, metering equipment, and switchgear. It is commonly used in urban developments, industrial parks, residential complexes, and temporary sites. The substation supports reliable voltage conversion and distribution while ensuring safety through enclosed components and standardized interfaces.
Key Benefits of IP68‑Certified Underground Cable Junction Boxes
An Underground IP68 Protection Cable Docking Box is a specialized enclosure designed for connecting and safeguarding electrical or communication cables below ground level. Constructed from durable, non‑corrosive materials such as polyethylene or polypropylene, the enclosure features an IP68 rating, ensuring complete dust ingress protection and water resistance under continuous submersion up to specified depths. This level of sealing prevents moisture, soil particles, and pests from compromising cable terminations.
Inside the docking box, preconfigured mounting points and cable gland ports accommodate various cable diameters. The interior often includes removable partition plates or splice trays, allowing technicians to organize and secure splices, joints, or connectors neatly. A hinged or removable lid provides easy access for installation and maintenance while preserving the enclosure’s protective characteristics once closed.
Applications span telecommunications, fiber‑optic networks, street lighting circuits, and industrial power distribution systems. In urban infrastructure projects, these boxes facilitate underground cable routing without disrupting surface activities. On construction sites, they offer a safe, temporary solution for connecting power tools and lighting equipment. Their resistance to mechanical impact and environmental stress reduces the risk of unexpected failures.
Installation typically involves burying the box at a shallow depth, backfilled with sand or fine aggregate to cushion against soil compaction. Ground markers or detectable tapes above the box location assist future excavation efforts. Routine inspections focus on verifying seal integrity and checking for signs of condensation or mechanical damage.
Design and Benefits of Subsurface Box‑Type Transformers
An Underground Box Transformer is a compact, metal‑clad unit designed to step down high‑voltage distribution lines to usable low‑voltage levels within an underground setting. Encased in a heavy‑duty, corrosion‑resistant housing, the transformer core and windings are immersed in insulating oil or epoxy resin, which provides cooling, dielectric strength, and protection against moisture ingress.
The enclosure incorporates cooling radiators or fins externally, allowing heat dissipation to the surrounding soil. Pressure relief devices and monitoring ports ensure safe operation by venting gases in overpressure scenarios and permitting oil sampling for preventive maintenance. Cable terminations are made through sealed porcelain or polymer insulators mounted on the tank cover, directing incoming high‑voltage cables and outgoing low‑voltage feeders into separate compartments. This segregation enhances safety during live‑line work.
Underground box transformers are installed below grade in concrete vaults or precast chambers, often located in residential neighborhoods, commercial districts, or industrial parks. Their placement beneath roadways or landscaped areas preserves surface aesthetics and frees up valuable real estate. Distribution networks benefit from reduced exposure to weather‑related outages and lower visual impact compared to overhead transformers.
Routine maintenance involves periodic oil testing for dielectric strength, infrared inspections of cable connectors, and torque checks on bolted joints.


 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 


















