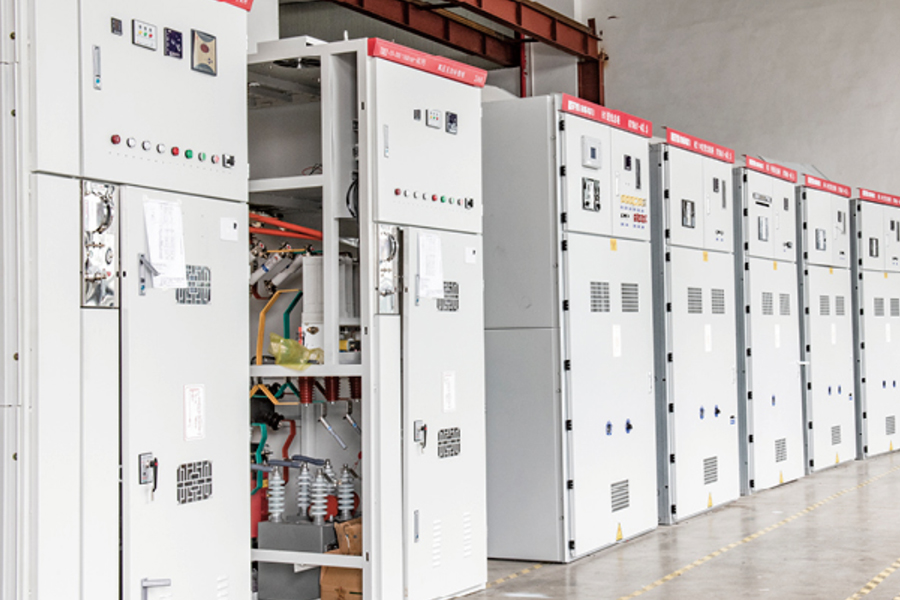
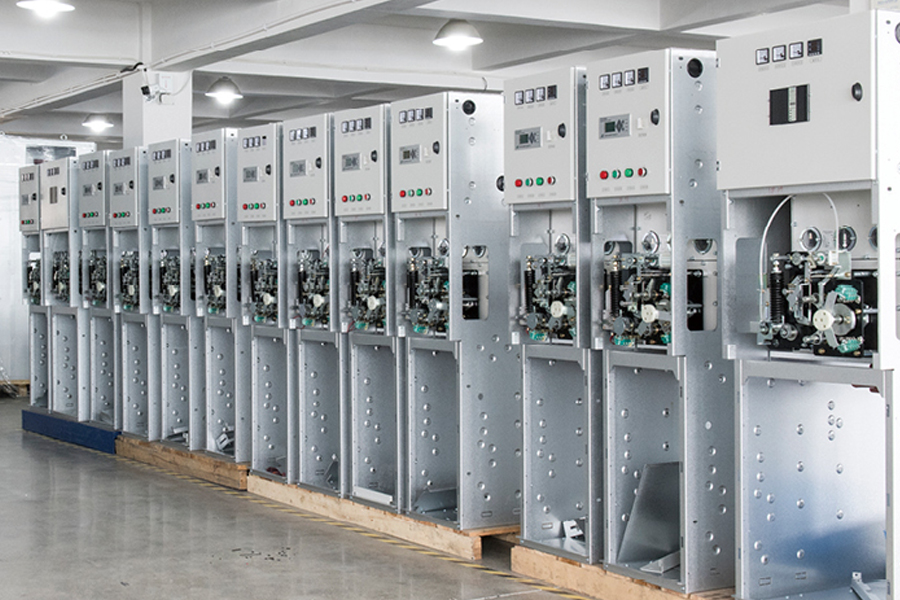
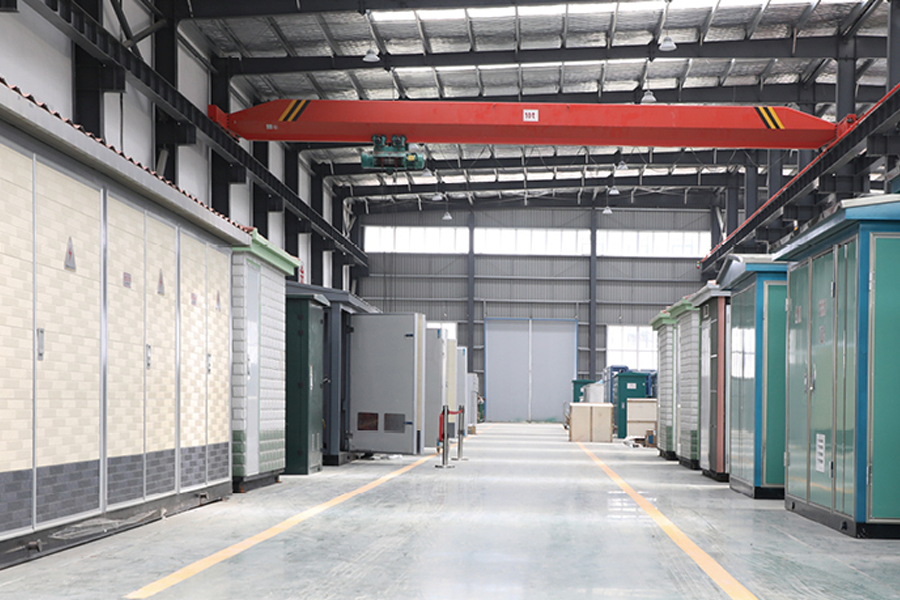
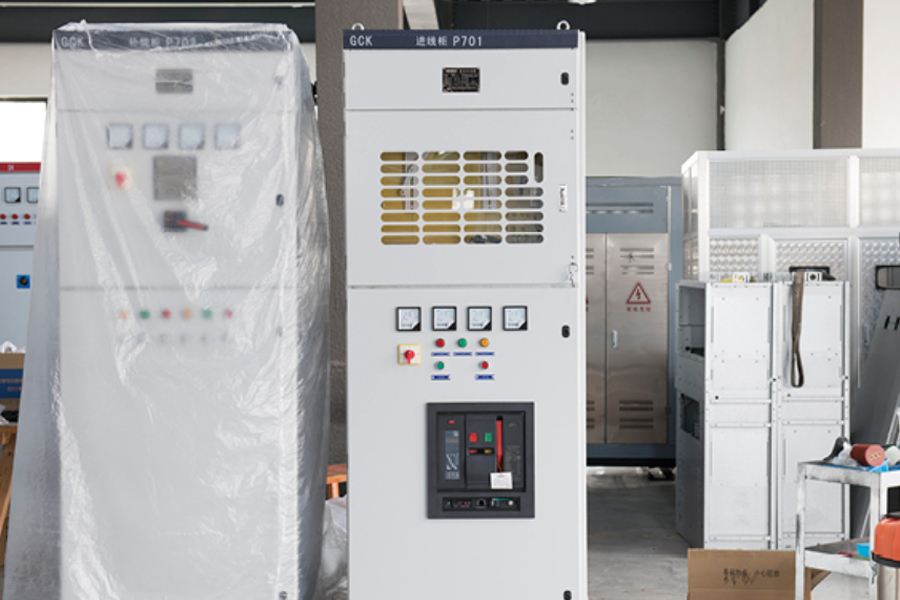
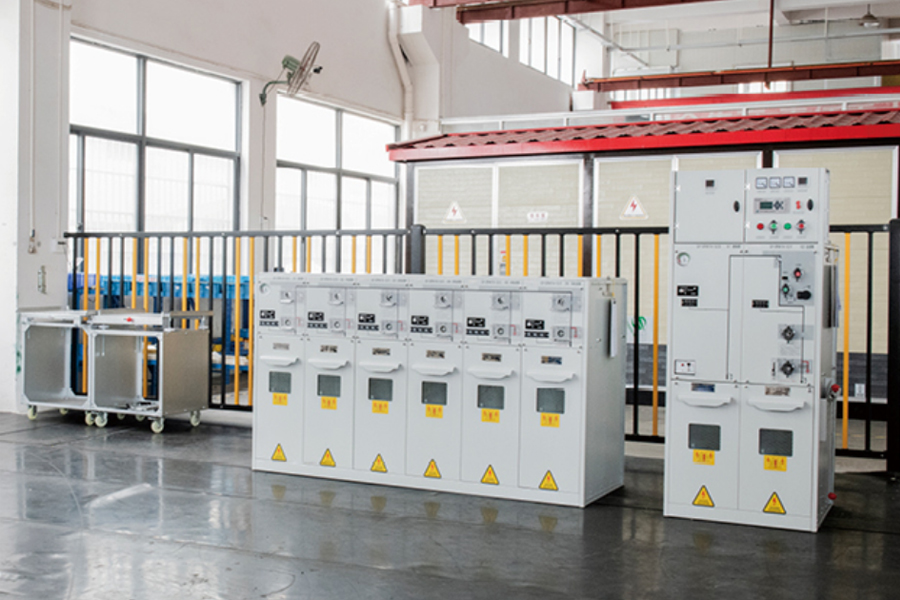
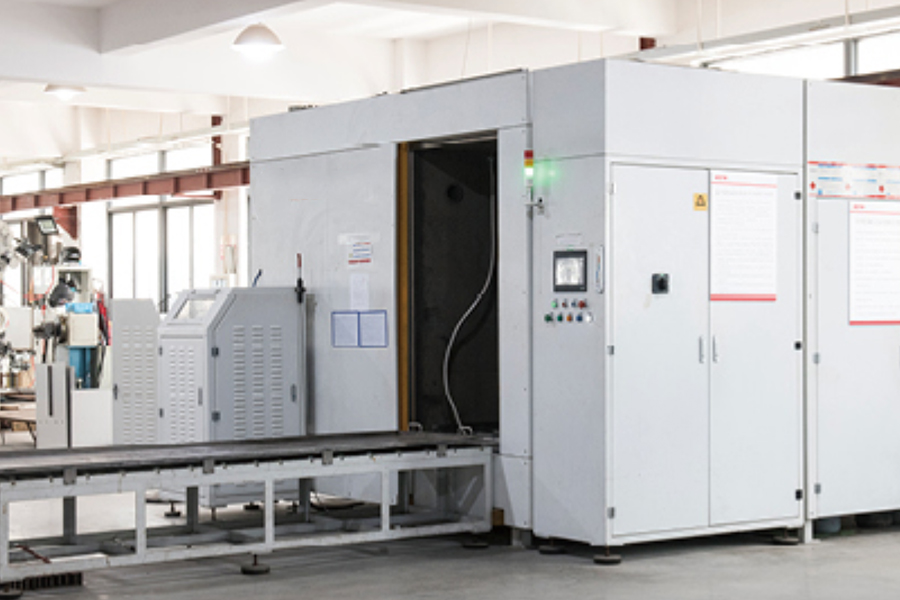
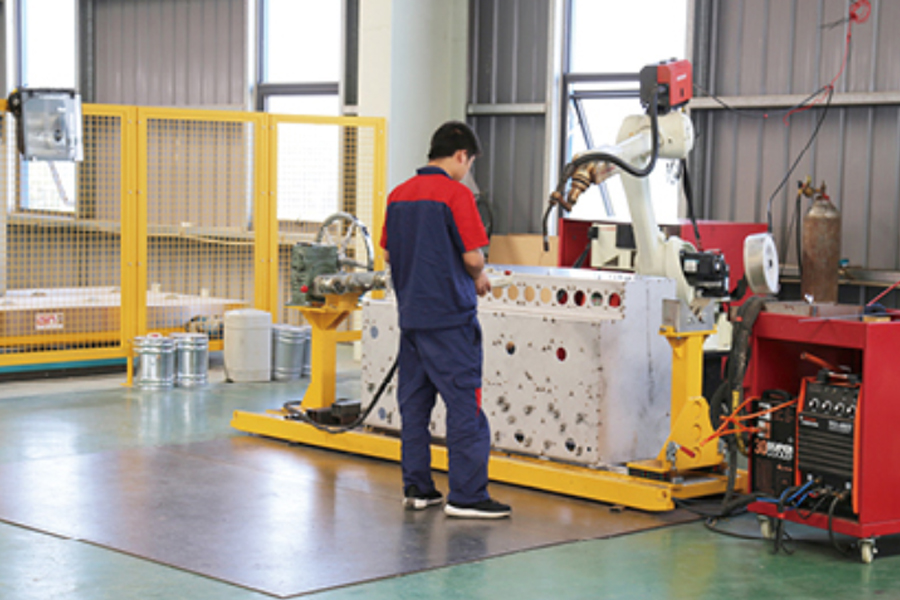
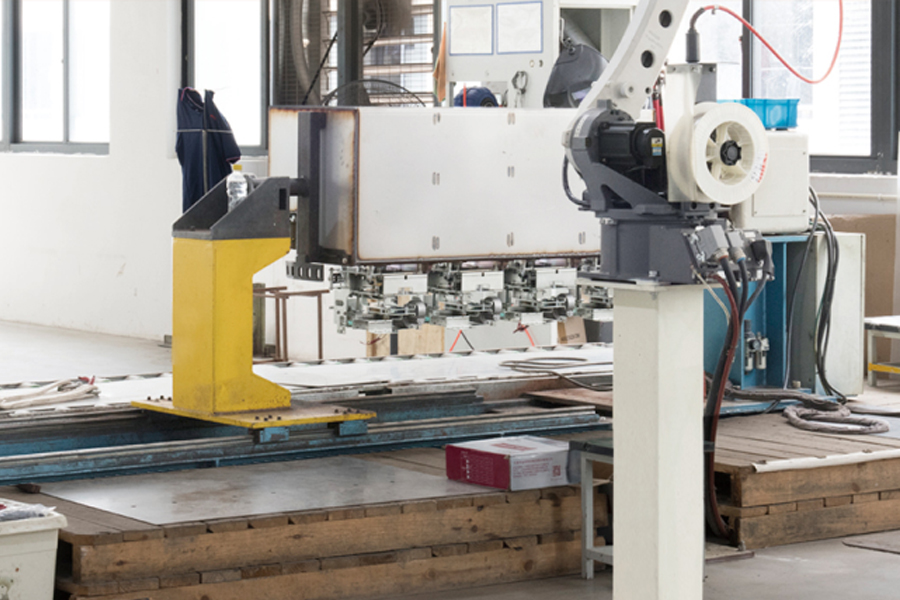
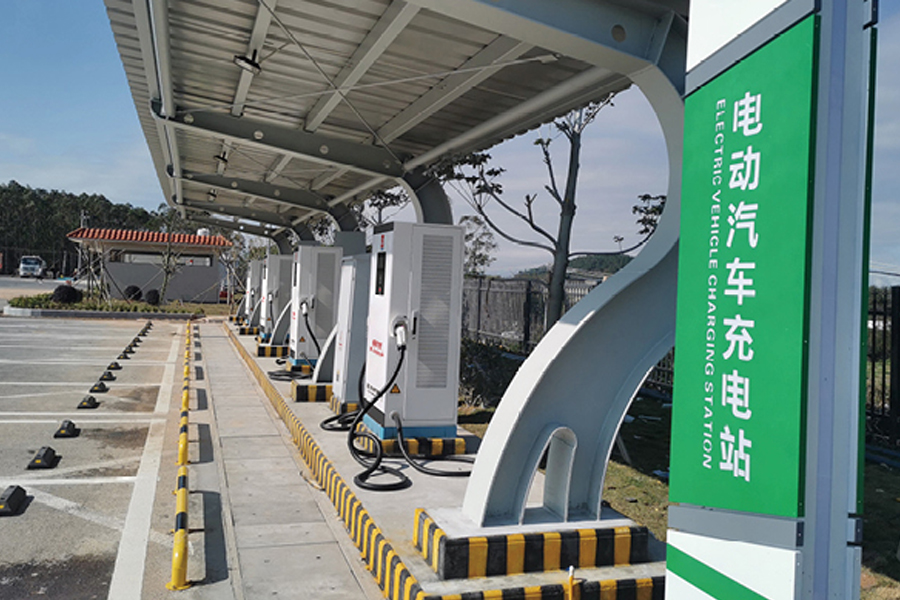
Distributed photovoltaic power stations have moved from pilot projects to widely deployed energy assets across residenti...
READ MOREMobile Energy Storage Charging Pile Factory
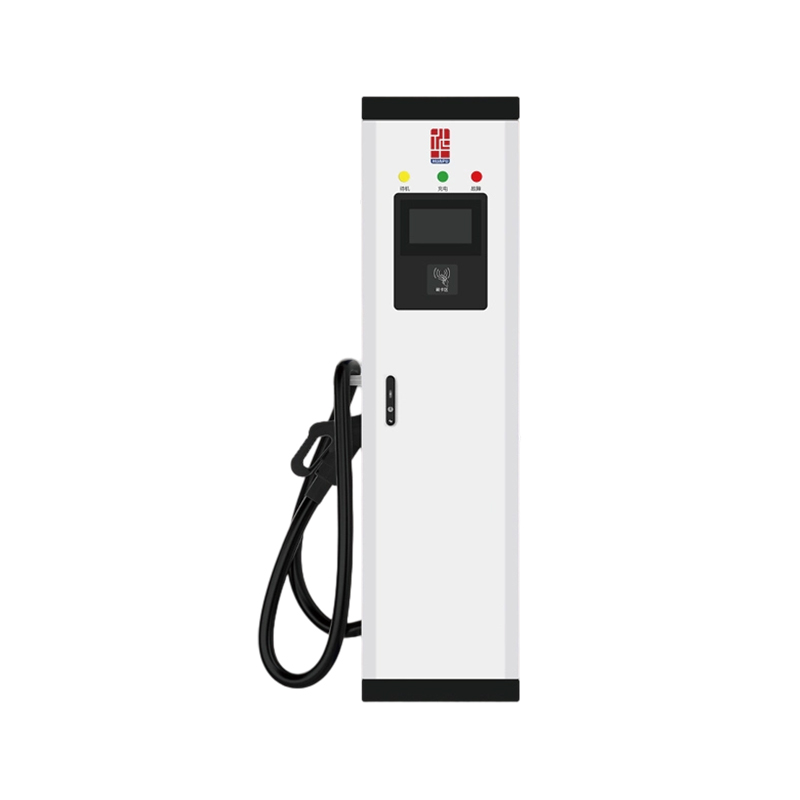
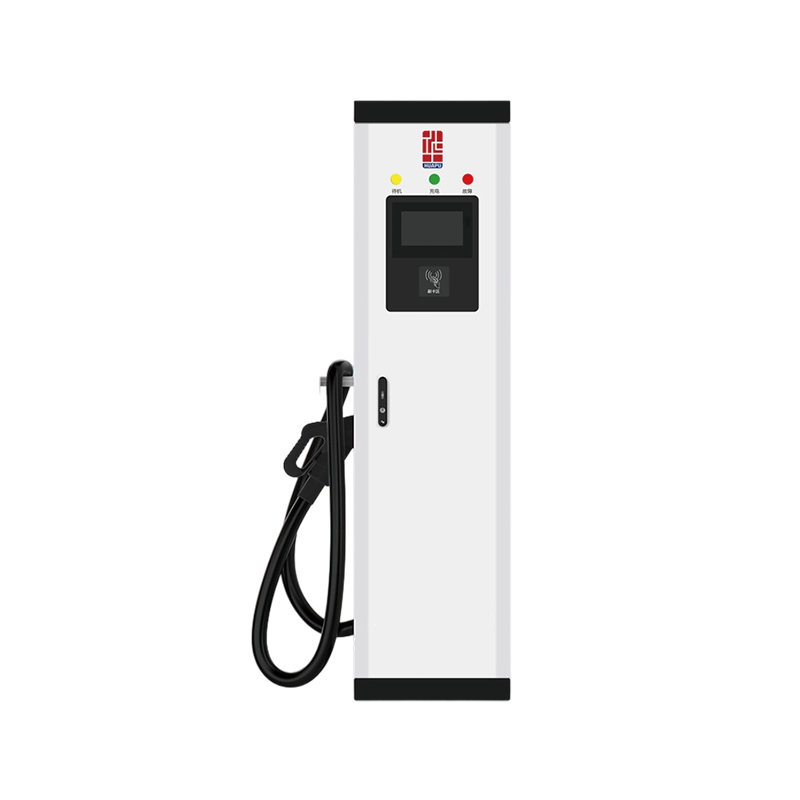
The New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Floor Charging Pile is an innovative charging solution designed to meet the growing demand for electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure in residential, commercial, and public environments.
Advantages:
One of the primary advantages of the NEV Floor Charging Pile is its user-friendly and accessible design. Unlike wall-mounted units that may limit placement, the floor-mounted structure allows flexible installation in open spaces such as parking lots, garages, and service areas. It supports high-power charging, significantly reducing the time required to charge a vehicle. Built-in safety protections, such as over-voltage, over-current, and leakage detection, ensure secure usage for both vehicles and users. Furthermore, the system supports smart metering and remote monitoring, allowing operators to manage energy consumption, billing, and maintenance more efficiently. With support for multiple charging protocols, the charging pile is compatible with most EVs on the market, ensuring wide usability.
Features :
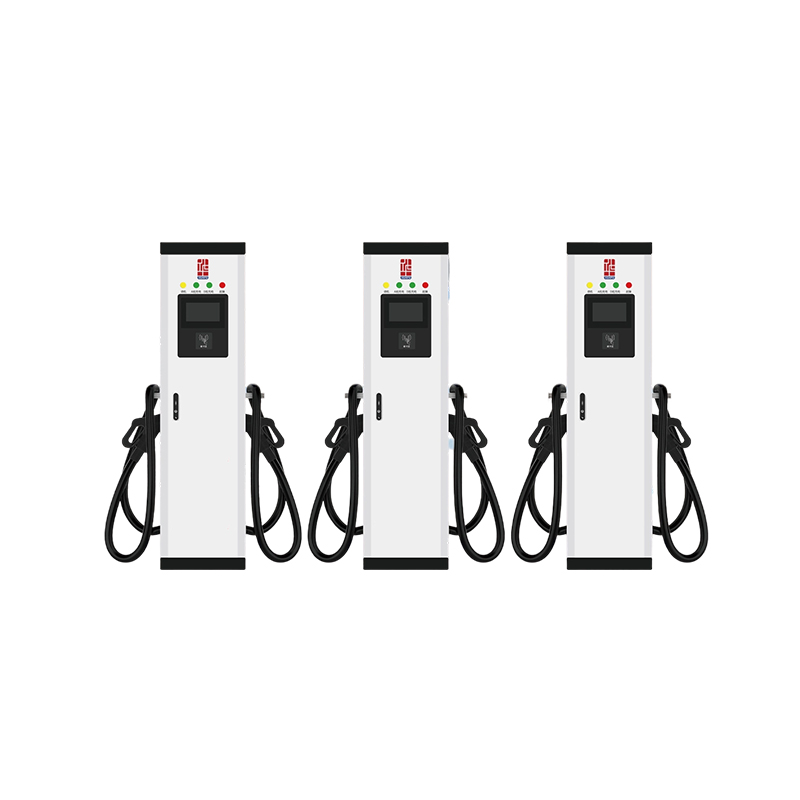
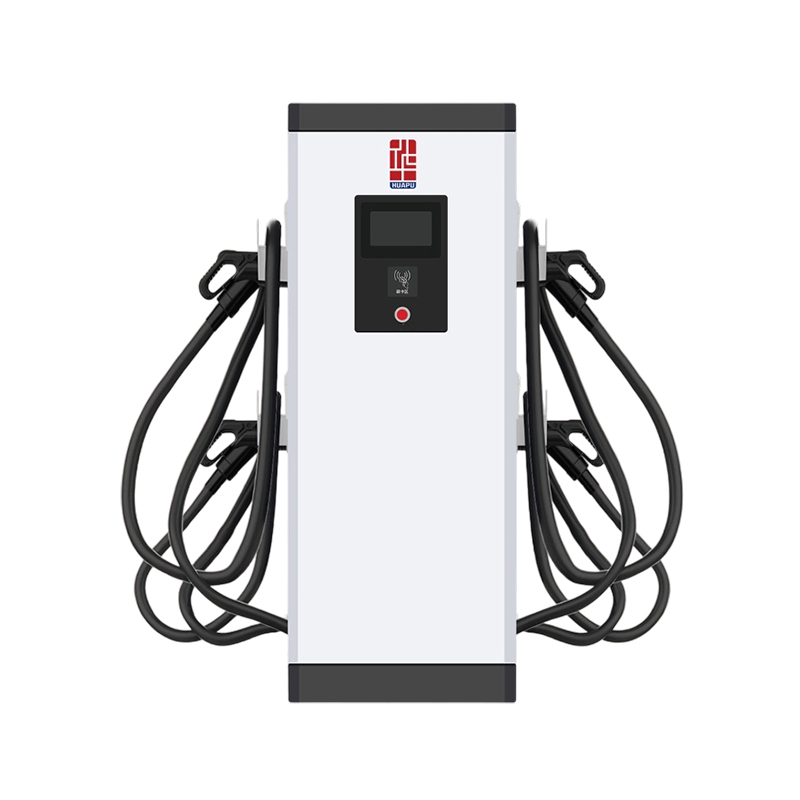
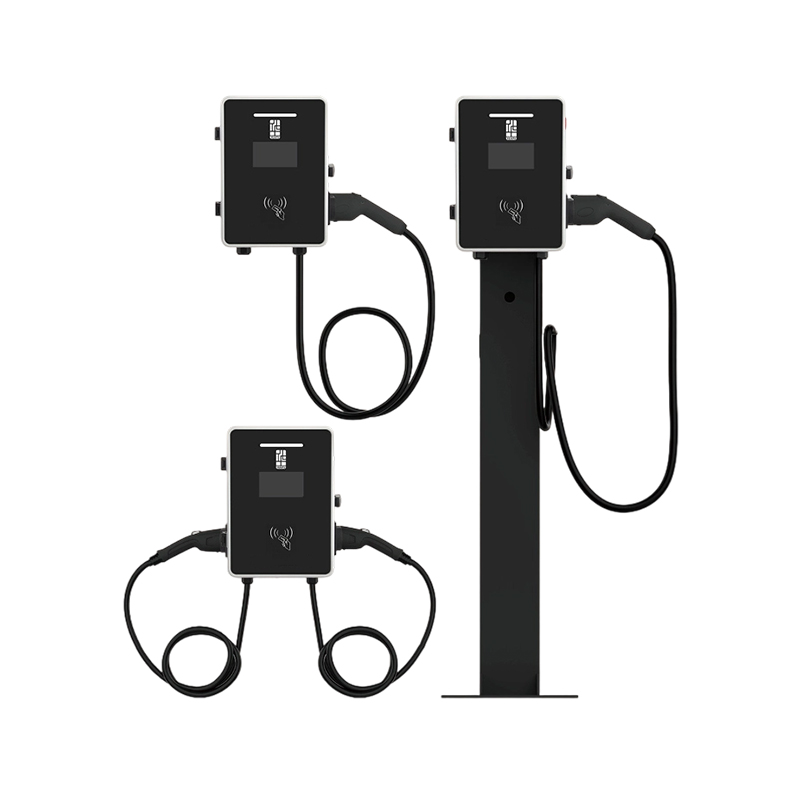
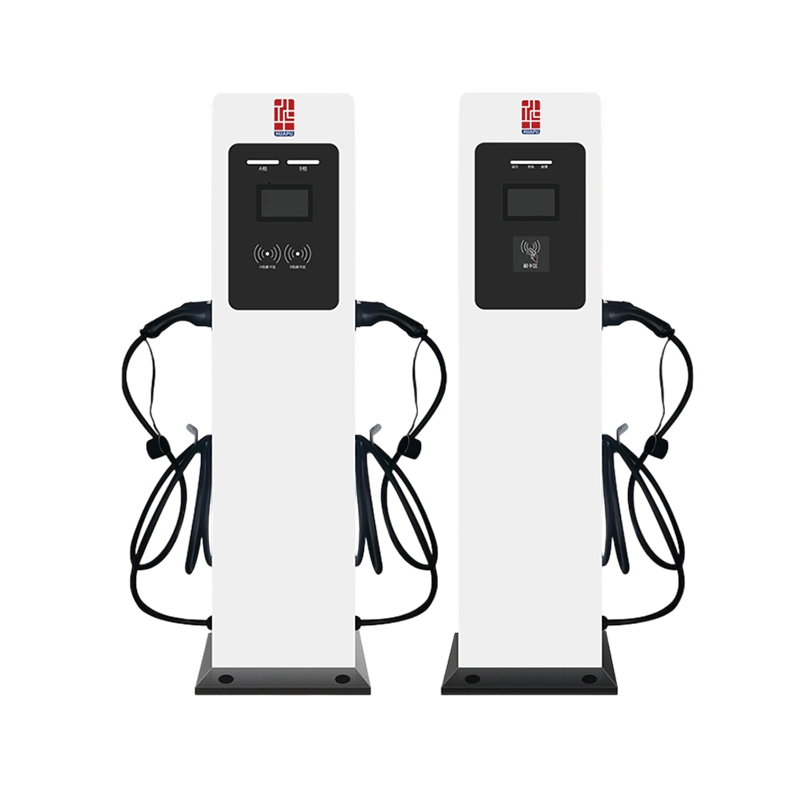
The layout-focused design of the NEV Floor Charging Pile prioritizes efficient space usage and intuitive placement. Its compact vertical structure minimizes the ground footprint, making it ideal for areas with limited space or high vehicle turnover. The sturdy base ensures stability under various weather conditions and frequent use. Cable management is optimized through an integrated reel or hanger system, preventing tripping hazards and extending cable life. Optional dual-gun configurations allow simultaneous charging of two vehicles, enhancing throughput in high-demand locations. The charging pile can be aligned in rows or clusters to support organized and scalable installations in large parking areas, while its modern design blends well with urban architecture.
Search
Categories
-
New Energy Power Distribution Equipment(6)
-
Box Type Substation(3)
-
Cable Branch Box/Switch Station(3)
-
High Voltage Switchgear (23)
-
Low Voltage Switchgear(16)
-
Engineering Vacuum Circuit Breaker(2)
-
New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile(9)
-
Commercial Energy Storage(3)
-
Photovoltaic Complete Box(8)
-
High Voltage Arrester(54)
-
-
Integrated photovoltaic inverters have become a central component in many solar power installations, combining power con...
READ MORE -
Photovoltaic modules are evaluated primarily by their electrical performance, durability under environmental stress, and...
READ MORE -
Thermal management is a broad concept in electronics and industrial systems, encompassing various cooling methods such a...
READ MORE
A New Energy Vehicle Floor Charging Pile is a ground‑mounted charging station designed to supply electric vehicles with power in parking lots or residential garages. The unit features a durable pedestal enclosure housing power electronics, a charging controller, and safety devices such as residual current monitoring. A tethered charging cable with a standardized connector allows easy linking to the vehicle’s inlet. Users initiate charging via a control panel or mobile application interface, which manages authorization, start/stop commands, and status feedback. Installation involves anchoring the pile to a concrete base and connecting it to the local electrical network. Routine inspections focus on cable integrity, connector cleanliness, and proper operation of safety interlocks.
Operational Guide for Mobile Energy Storage Chargers
A Mobile Energy Storage Charging Pile is a transportable station that combines battery storage with electric vehicle (EV) charging functionality. Housed within a weatherproof cabinet on a trailer or skid frame, it integrates lithium‑ion or similar battery modules, power conversion inverters, and a charging interface. During periods of low demand or when connected to a local grid, the unit’s batteries are charged via AC or DC input. When EVs require power—such as at remote events, construction sites, or emergency response locations—the pile switches to discharge mode, supplying electricity through standard charging connectors.
The system control unit manages state‑of‑charge, monitors battery health, and regulates charge/discharge currents to ensure safe operation. A user interface panel displays real‑time data including available capacity, voltage levels, and charging status. Some models support load‑shifting strategies, drawing power from the grid during off‑peak hours and delivering stored energy at peak times to reduce demand charges. Safety components include overcurrent protection, thermal management systems, and ground‑fault monitors to prevent hazardous conditions.
Deployment involves securing the unit on a level surface, connecting to a suitable power source for initial charging, and positioning cable reels for vehicle access. Mobility features such as hydraulic stabilizers or locking castors allow quick setup and repositioning. Routine maintenance covers inspection of battery modules, verification of cooling fans or liquid‑cooling circuits, and testing of protective relays.
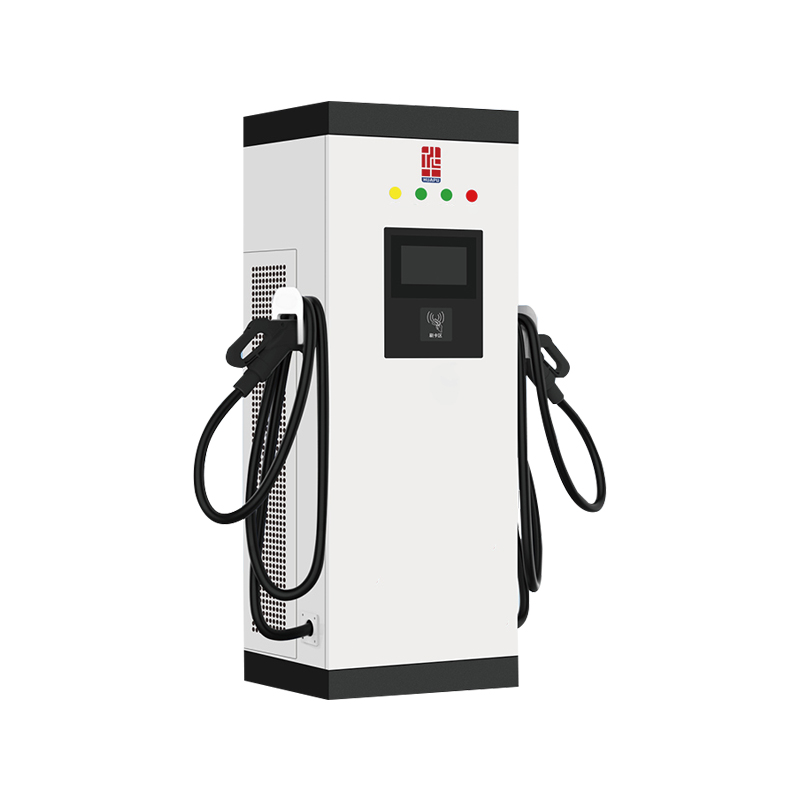
Key Components of a Single‑Unit DC Charging Station
An Integrated DC Charging Pile is a fixed‑position station designed to deliver direct current (DC) directly to an EV’s battery at high power levels. The unit combines rectification, power factor correction, DC–DC conversion, and cooling subsystems into a single enclosure. Incoming AC supply is one conditioned by an active front end, then converted to a stable DC bus. Power electronics modules adjust voltage and current to match the vehicle’s battery requirements. Cooling—via air or liquid circuits—maintains component temperatures within safe operating limits.
The charging interface conforms to established DC standards, offering output levels that typically range from 50 kW up to several hundred kilowatts. A user panel allows drivers to initiate transactions through RFID cards or mobile apps and displays charging parameters such as output voltage, current, and estimated completion time. Communication interfaces (CAN, Ethernet) support connection to charging management systems, enabling load balancing, remote diagnostics, and billing integration.
Installation requires mounting the pile on a reinforced concrete foundation, grounding the enclosure, and connecting to a three‑phase HV supply line sized to accommodate peak power draw. Cable management systems—retractable or fixed—ensure ergonomic access to the vehicle inlet. Safety features include residual current detection, automatic shutdown on fault conditions, and emergency stop buttons. Regular servicing involves inspection of power modules, verification of insulation resistance on DC cables, and replacement of air filters or coolant.


 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  русский
русский  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 
























